What is Project Management?
Project management is a systematic approach that organizations employ to plan, organize, and allocate resources in order to complete specific tasks or projects. Two commonly used methodologies in project management are traditional and agile project management.
Traditional Project Management
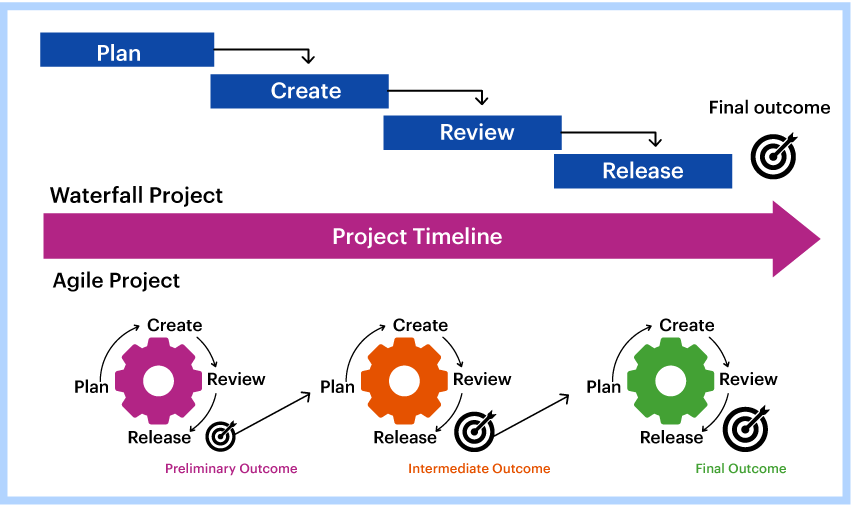
Traditional project management follows a sequential and linear approach. It typically consists of initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure phases. It is crucial to define the project scope and requirements at the project's outset.
Benefits of Traditional Project Management
-
Clear Expectations: The planning phase in traditional project management allows for estimating costs, schedules, and required resources. Clear expectations ensure that everyone involved in the project, including project stakeholders and team members, understands the timeline and anticipated outcomes.
-
Defined Responsibilities: Each individual has a specific role and responsibility within a traditional project management framework. Overlapping tasks and duplication are minimized, ensuring efficient teamwork and clarity regarding expectations.
-
Documentation: Traditional project management emphasizes the importance of clear documentation at every stage, starting from the planning phase. Project documents serve as reference materials for all stakeholders and can guide future projects and project managers.
-
Accountability: The project manager is responsible for ensuring that all team members meet their milestones and complete the project on time. This model establishes a clear line of accountability and encourages stakeholders to approach the project manager with any concerns or update requests.
-
Control: Traditional project management follows strict requirements for each phase before progressing to the next. This ensures adherence to the original plan, and any changes or deviations require approval from the project manager after a thorough review of potential impacts.
Agile Project Management
Agile project management is a more recent methodology that emphasizes collaboration, flexibility, and iterative releases throughout the project lifecycle. Unlike the rigid structure of traditional project management, agile relies on close team collaboration, external feedback, and adaptability.
Benefits of Agile Project Management
-
Flexibility: Agile project management allows for updating requirements, shifting priorities, and adjusting resources as needed. Projects are divided into shorter iterations within the larger project, enabling more frequent updates with less disruption to the overall goal. Prioritizing new features or requirements while delaying others based on needs demonstrates an organization's responsiveness to end-user requirements.
-
Early and Consistent Delivery: Through frequent updates and iterations that address stakeholder needs, organizations can build trust and credibility with their clients or stakeholders. Regular check-in meetings during the project provide opportunities for feedback and course correction.
-
Transparency: Agile projects promote transparency by ensuring that team members are aware of their assigned tasks and the progress of other team members. This transparency fosters innovation, empowers team members, and helps leaders understand all aspects of the project.
-
Collaboration: Agile project teams can include stakeholders, members from different departments, and individuals at various levels within the organization who may not typically be involved in project management. This diverse collaboration helps improve the quality of deliverables, systems, and processes, aligning them with the actual needs of end-users.
Choosing between Traditional and Agile
The size of the project and the nature of the department play a significant role in determining which methodology to adopt. Larger initiatives and organizations often prefer the traditional method for its established framework that reliably delivers expected results within budget and on schedule. Agile methodologies are often more suitable when requirements are less clear or when organizations are smaller and encourage collaborative decision-making.
Risk assessment is another factor to consider when choosing a methodology. If a project carries a high level of risk or if requirements are subject to change, an agile framework allows for quick issue resolution within shorter iterations. On the other hand, critical projects with limited room for error may benefit from the extensive planning and documentation of the traditional method, ensuring minimal scope changes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both traditional and agile project management approaches have their distinct advantages and are suited for different project scenarios. Traditional project management provides a structured and predictable framework, ensuring clear expectations, defined responsibilities, and controlled processes. It is best suited for projects with well-defined requirements, fixed timelines, and a limited need for flexibility.
On the other hand, agile project management offers flexibility, adaptability, and frequent feedback loops, enabling organizations to respond quickly to changing requirements and customer needs. It promotes collaboration, transparency, and early and consistent delivery of value. Agile is ideal for projects with evolving requirements, high customer involvement, rapidly changing market conditions, and a need for continuous improvement.
Choosing the right project management methodology depends on various factors, including project size, department culture, risk level, and the nature of the project itself. Understanding the key differences between traditional and agile project management empowers project managers to make informed decisions and select the most appropriate approach for their specific projects.
Ultimately, successful project management requires a flexible mindset, a deep understanding of project requirements, and the ability to adapt to the unique needs of each project. By leveraging the strengths of both traditional and agile project management methodologies, organizations can optimize their project outcomes and drive success in today's dynamic business environment.